Technology‑Enhanced Learning (TEL) in GMU

Innovating Education. Empowering Learners. Transforming Healthcare.
At Gonabad University of Medical Sciences (GMU), Technology‑Enhanced Learning (TEL) stands at the heart of our educational transformation. It embodies GMU’s commitment to modernizing medical education through innovation, accessibility, and evidence‑based digital methodologies—creating a bridge between learning and practice in the 21st century.
Vision and Philosophy
TEL at GMU follows the principle that technology should serve humanity and health. It does not simply digitalize education—it humanizes innovation by integrating technology into ethical, patient‑centered, and socially accountable teaching.
Through the TEL initiative, GMU ensures that medical sciences are delivered interactively, inclusively, and sustainably—developing professionals who are competent in both science and empathy.
Digital Infrastructure and Smart Classrooms
GMU has successfully initiated smart learning environments equipped with:
- Virtual and Hybrid Classrooms, enabling synchronous and asynchronous access to medical lectures.
- E‑Learning Platforms integrated with AI tools that analyze learning behavior and personalize students’ progress.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Simulation Labs allow students to perform and repeat medical procedures safely before entering real‑life clinical settings.
- Tele‑Education Systems provides remote training and real‑time experience exchange with affiliated teaching hospitals.
E‑Learning & Digital Education
GMU leverages advanced E‑Learning technologies to foster accessibility, flexibility, and innovation in health sciences education. Through its Learning Management System (LMS), students and educators engage in synchronous and asynchronous learning—encompassing lecture videos, simulation modules, and digital clinical cases.
This hybrid approach supports the university’s Vision 2030–2040 by ensuring sustainable, technology‑enabled education aligned with international standards.
E‑Learning modules are fully integrated into the curricula of Medicine, Nursing, and Nutrition Sciences, promoting lifelong learning, interdisciplinary teaching, and personalized academic progression.
GMU continuously enhances its digital ecosystem through faculty training, AI‑enabled evaluation tools, and collaboration with global institutions—positioning itself as a regional leader in tele‑education and digital health pedagogy.
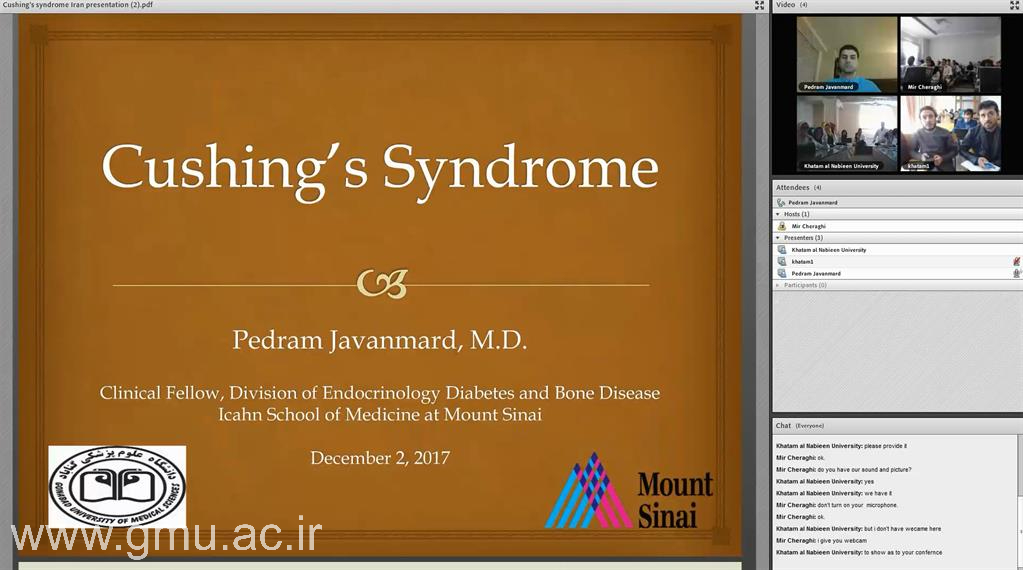
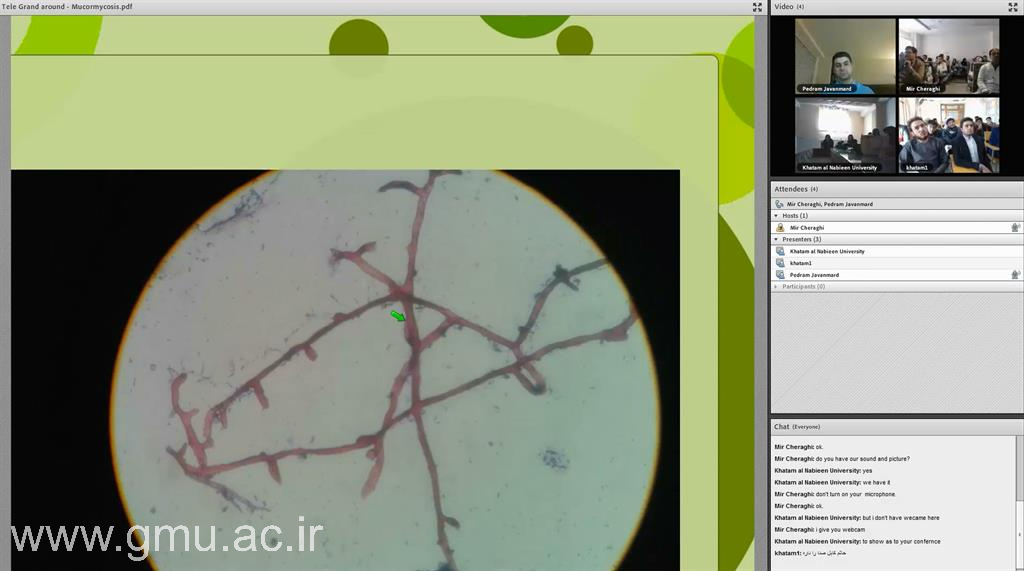
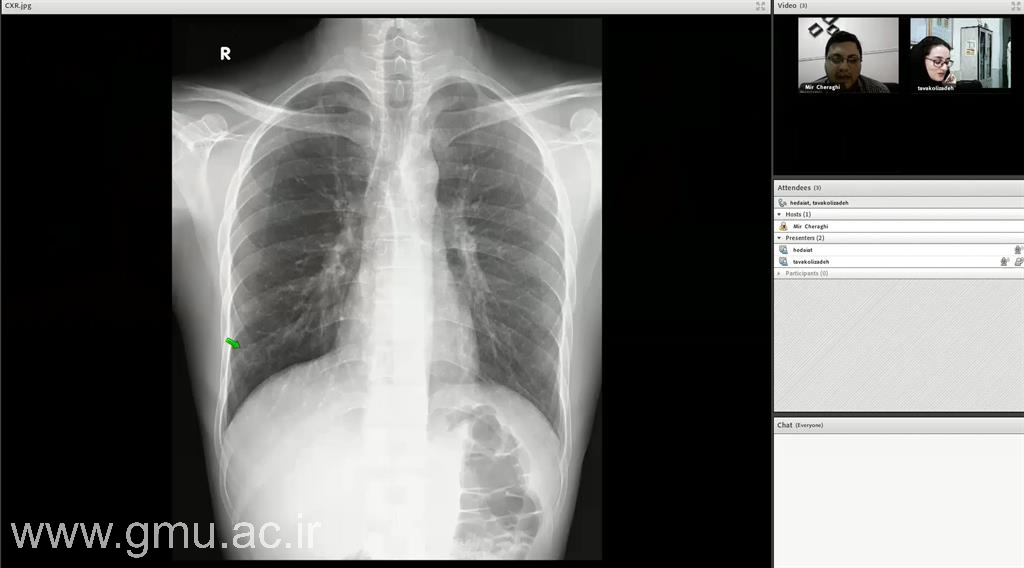
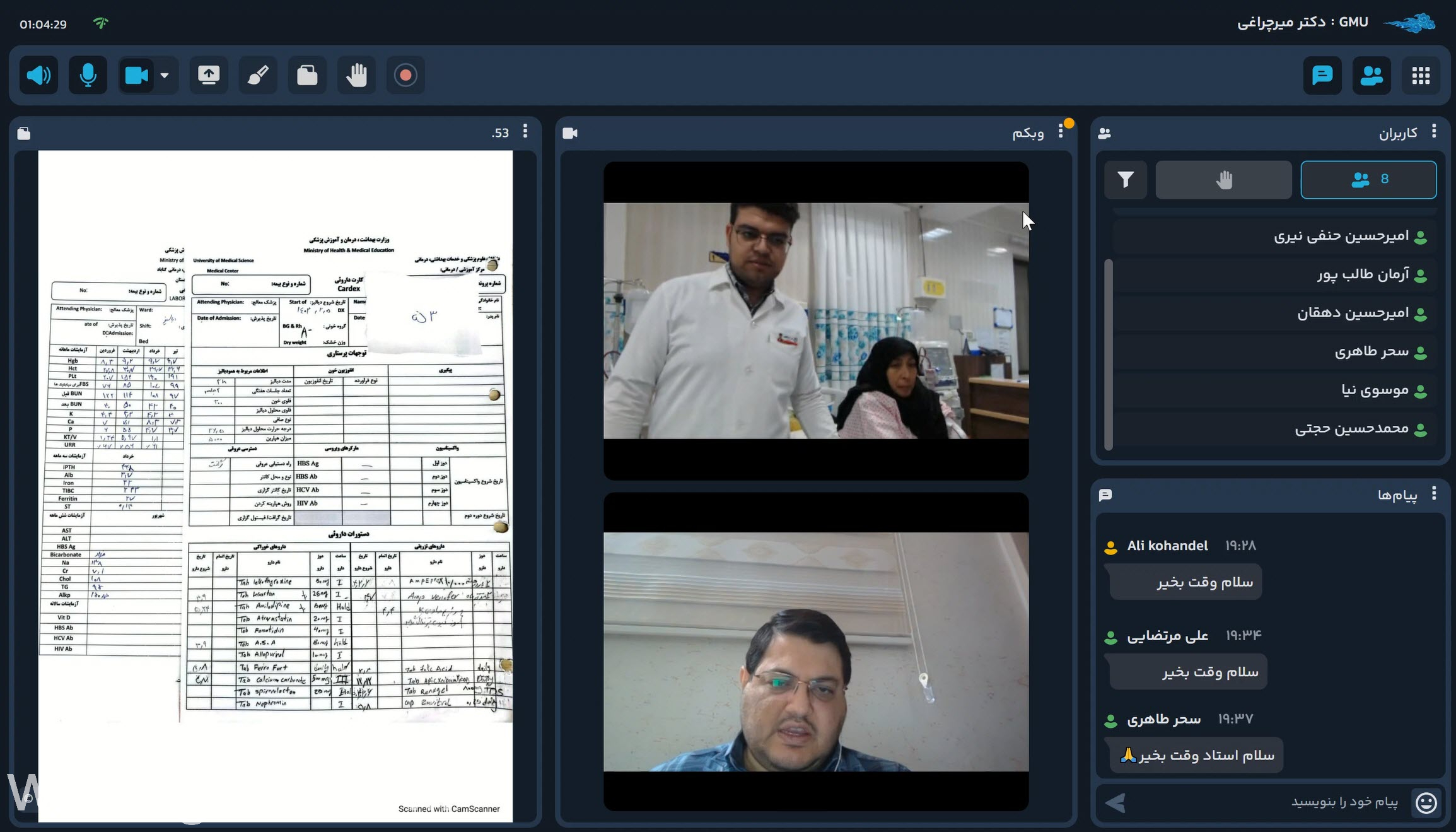
Tele Grand Rounds & Online Morning Reports
Tele Grand Rounds
The Tele Grand Round program at Gonabad University of Medical Sciences (GMU) integrates clinical excellence with digital innovation, enabling faculty, residents, and international collaborators to participate in real-time, multidisciplinary case discussions through secure telemedicine platforms.
These sessions build a dynamic clinical learning environment connecting GMU teaching hospitals with global academic centers. Each session features patient presentations, expert commentaries, and question–answer interactions emphasizing clinical reasoning, ethical decision-making, and international collaboration.
This initiative embodies GMU’s vision to bridge technology and human-centered medical education.
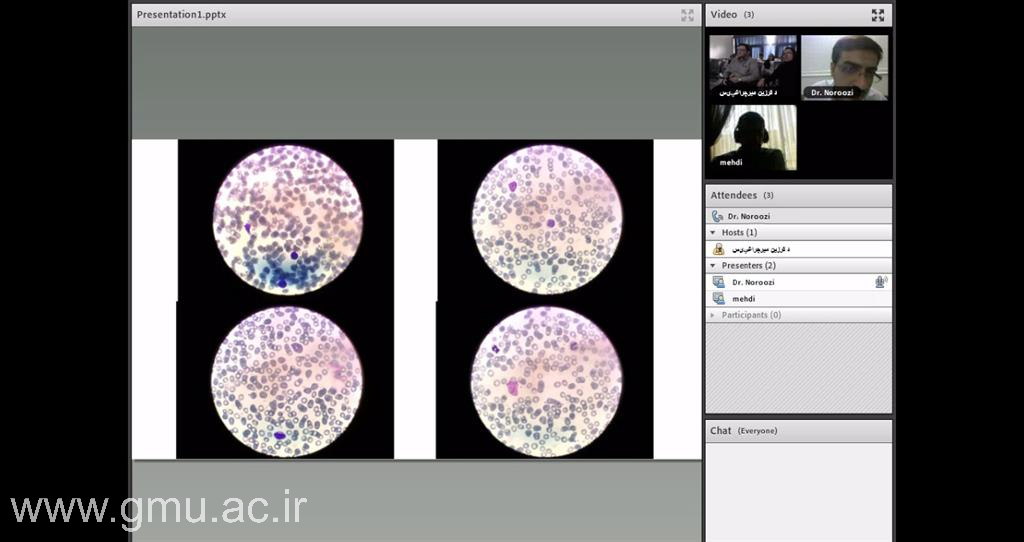
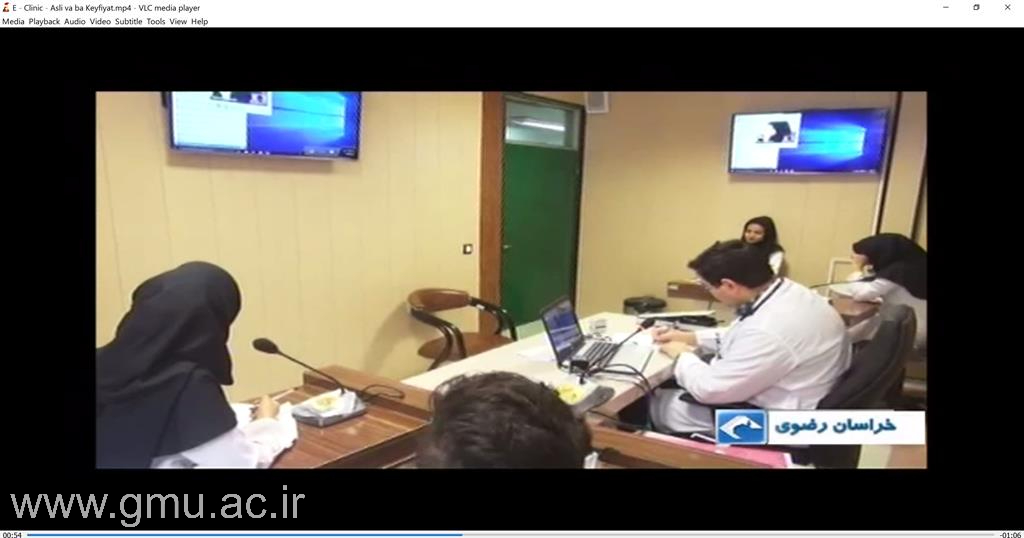
Online Morning Reports
As part of the university’s hybrid educational ecosystem, Online Morning Report complements the Tele Grand Round by facilitating daily clinical case analysis through integrated online platforms.
Students and residents connect remotely to review diagnostic approaches and management plans guided by attending physicians and educators.
This system strengthens interactive learning, continuity in clinical education, and rapid feedback cycles within GMU’s tele-education framework — ensuring that learners remain connected to real-time hospital activities even when off-site.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data in Learning
At Gonabad University of Medical Sciences (GMU), the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data analytics has transformed the delivery and evaluation of medical education. GMU ranks among the leading Iranian health universities, seeking to create data‑driven learning environments that personalize education and strengthen scientific performance.
Intelligent Educational Ecosystem
GMU is trying to establish a digital ecosystem where AI‑powered analytics continuously monitor student progress, assess knowledge patterns, and predict professional competency development. This system ensures that teaching strategies are adaptive, precise, and outcome‑oriented.
Data‑Driven Innovation for Future Medicine
Through continuous use of AI and Big Data, GMU prepares students for the future of healthcare—where analysis, prediction, and intelligent systems complement the art of medicine.
Learning becomes dynamic, evidence‑based, and personalized; scientific data transforms into insight; and technology becomes a tool for nurturing both human and planetary health.
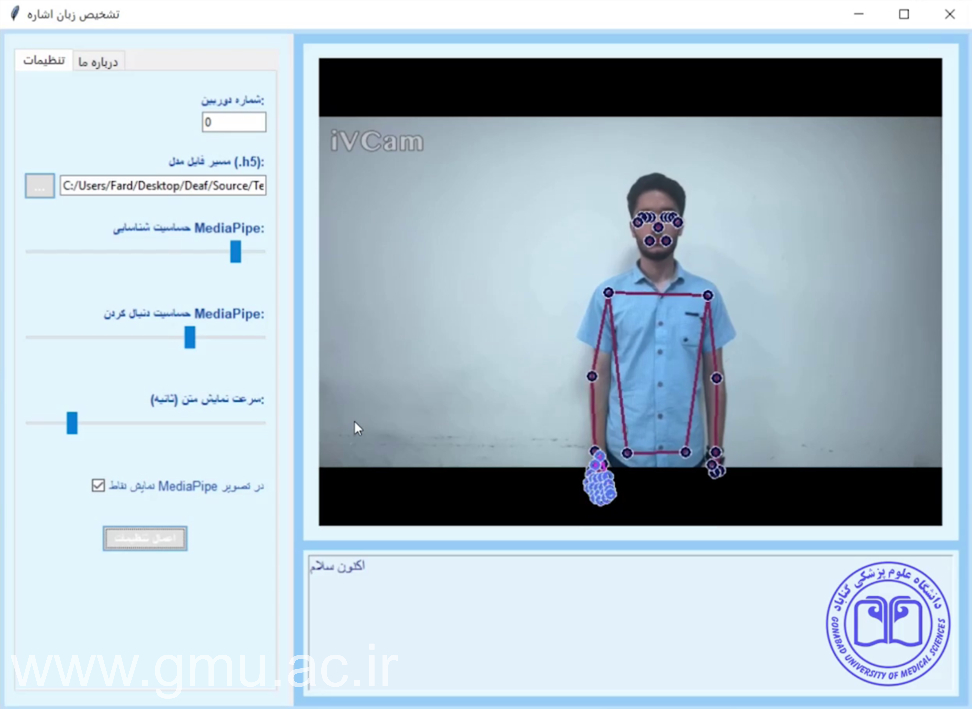
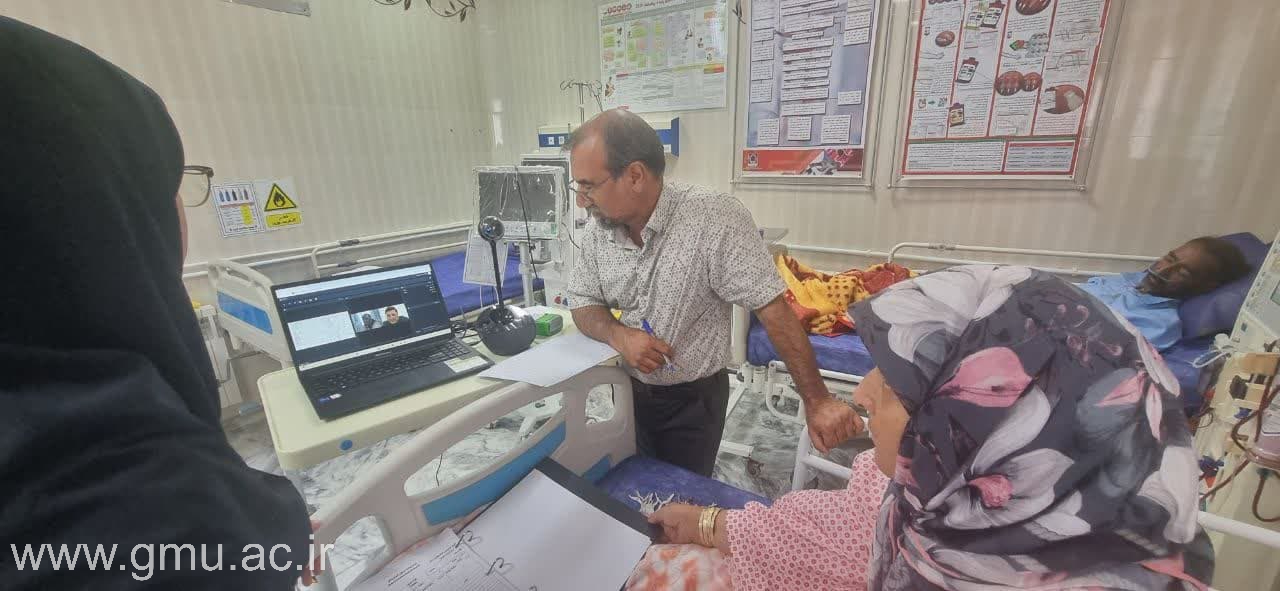
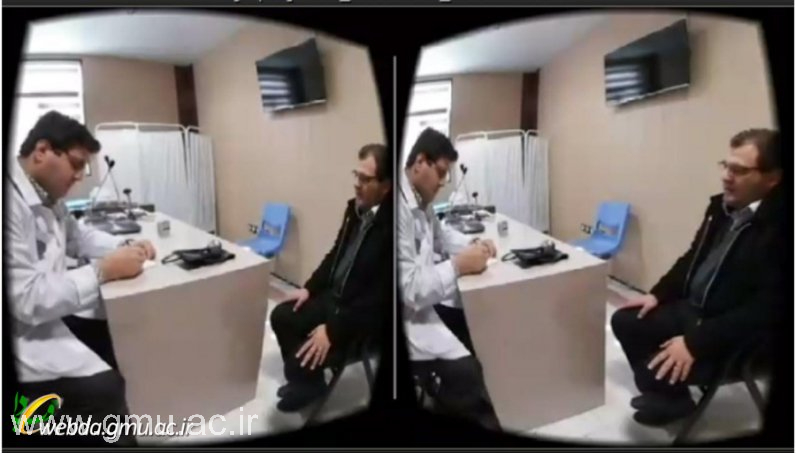
Telemedicine‑Based Learning
As an early adopter of Telemedicine in academic training, GMU integrates clinical tele‑consultation modules into its teaching programs.
Students experience patient interaction across distance settings, learning to deliver care through technology—a critical skill for future healthcare environments.
This feature extends GMU’s educational boundaries towards health equity and remote‑care accessibility, supporting underserved populations regionally and globally.
Academic Ecosystems and Faculty Development
Faculty members receive continuous professional training in Digital Pedagogy, AI Literacy, and Data Ethics, ensuring the responsible use of technology in education.
TEL also supports collaborative research across fields such as Gerontological Health, Planetary Health, and Occupational Health & Safety—connecting academic innovation to real human and environmental wellbeing.
Virtual, Augmented, and Holographic Systems in Medical Education
Integrating VR, AR & 3D Hologram for Clinical and Basic Sciences
Gonabad University of Medical Sciences (GMU) advances the transformation of medical education through immersive and interactive digital environments — utilizing Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and 3D Hologram systems.
These technologies serve as cornerstone tools for global teaching collaboration, skill simulation, and comprehensive understanding of biomedical concepts across disciplines.
Virtual Reality (VR): Clinical Simulation and Empathy Training
VR-based modules provide realistic encounters with patient care, anatomy, and surgical environments without the constraint of physical space.
Applications include:
- Clinical case immersion, enabling students to practice diagnosis and procedural flow within 360° environments.
- Empathy and communication training, enhancing patient-centered care through virtual interaction scenarios.
- Emergency medicine simulation, allowing repetitive practice in trauma management and resuscitation processes.
By combining data-driven modeling with narrative learning, VR helps to form resilient, reflective clinicians equipped for telemedical and global health frameworks.
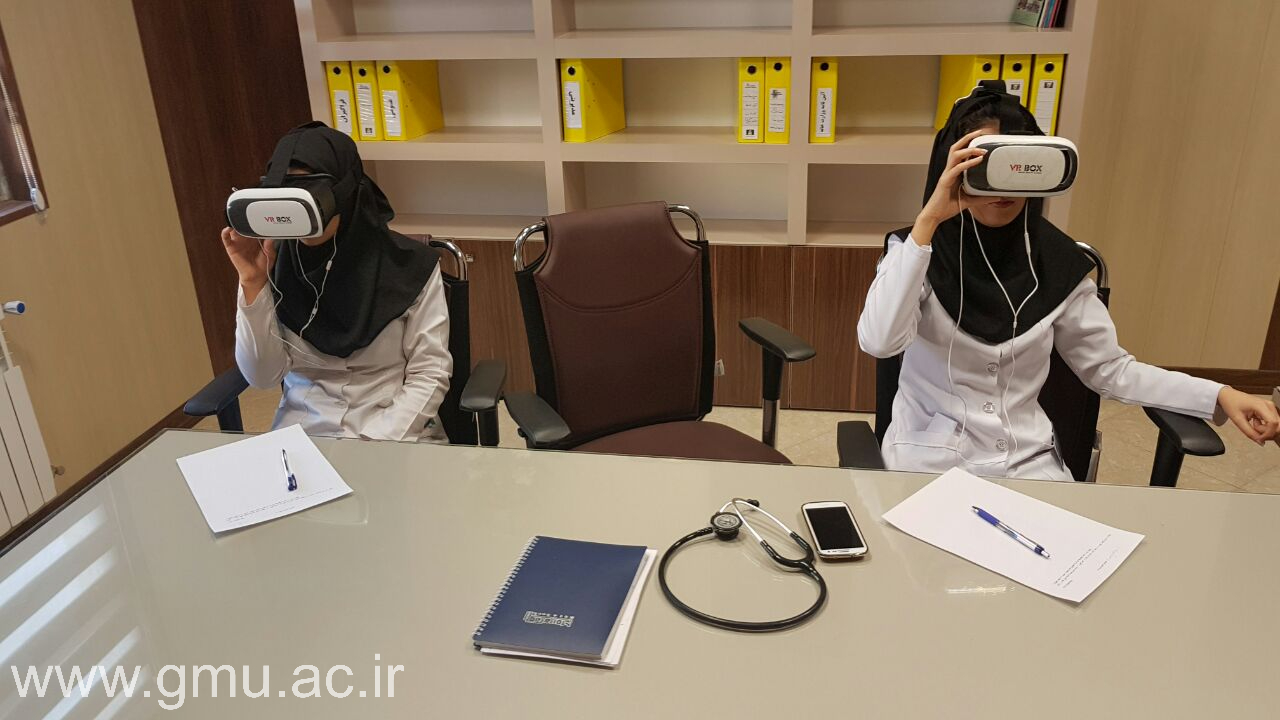




Augmented Reality (AR): Bridging Physical and Virtual Science
AR platforms at GMU merge digital anatomy and procedural steps over real-world views, promoting contextual learning in classrooms, hospitals, and community health settings.
In basic sciences, AR enables the dynamic visualization of molecular structures, histology slides, and organ systems over live instruments or printed materials.
Within clinical settings, AR supports surgical navigation, bedside instruction, and hybrid tele-mentoring with partner universities worldwide — strengthening international links in digital medicine.


3D Hologram: Affordable and Impactful Visualization
To democratize access to advanced visualization, GMU employs 3D Hologram technology, using optical projection to emulate full holographic effects without complex infrastructure.
Its real-world usage includes:
- Anatomical and physiological demonstrations at teaching hospitals and global exhibitions.
- Interactive conference showcases, illustrating diagnostic innovations and biomedical prototypes.
- Distance education displays, projecting real-time virtual instructors or anatomical models during tele-rounds.
These “hologram” units support low-cost internationalization, providing tangible immersion for audiences across borders and enhancing GMU’s visibility in global academic events.
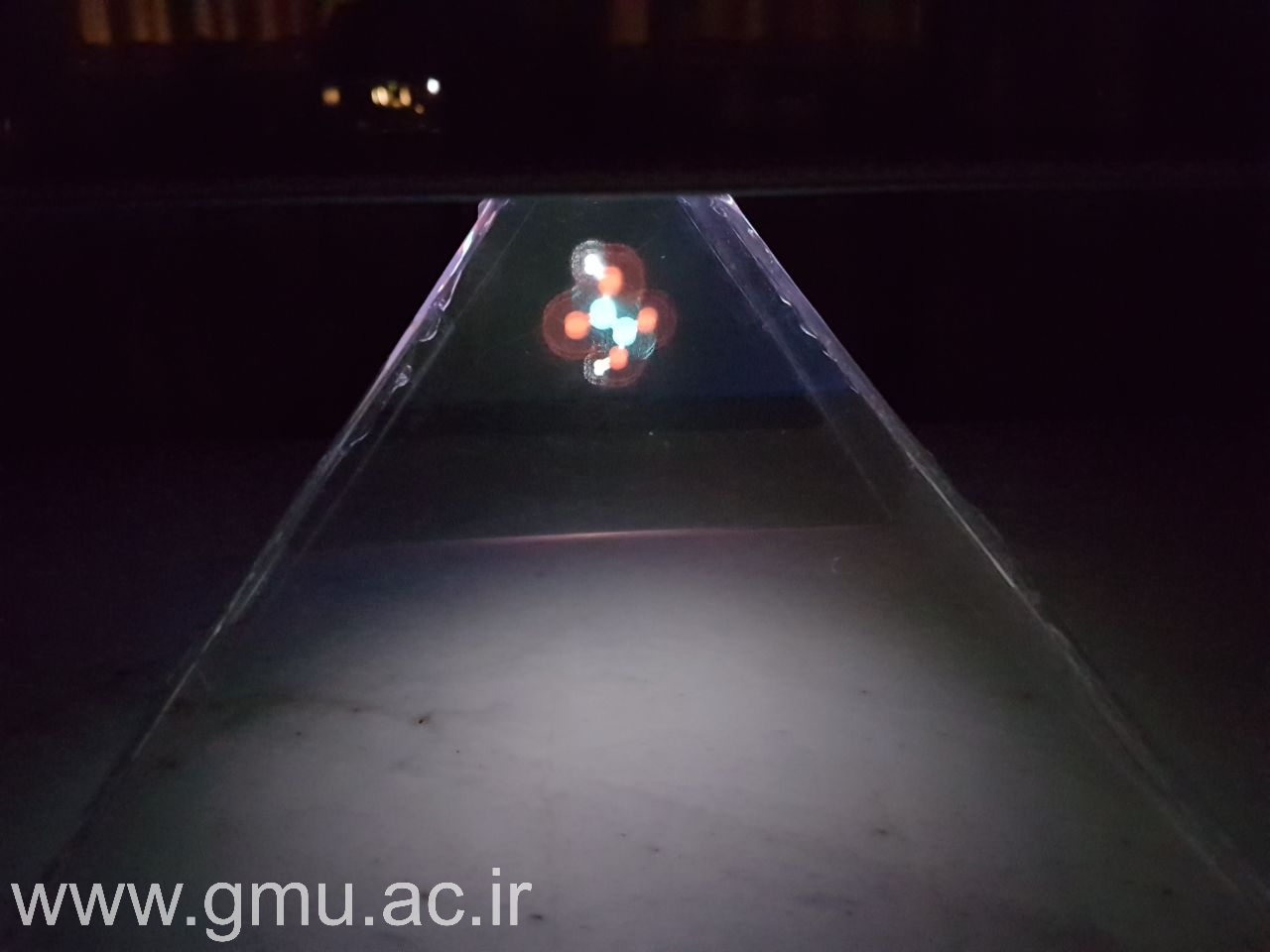

Integrative Research and Global Collaboration
GMU’s Digital Simulation Lab integrates VR, AR, and holographic design into cross-disciplinary research linking medical informatics, neuroscience, and tissue engineering.
Joint initiatives focus on:
- VR-based cognitive rehabilitation and virtual patient analytics.
- AR-enabled experiential anatomy in collaboration with international universities.
- Open-source hologram-based remote lectures and exhibitions for medical diplomacy.
Together, these efforts embody GMU’s philosophy of human-centered, technology-driven learning, strengthening the university’s identity as an innovator in medical education within Iran and across the region.
Immersive learning technologies for global medical excellence — reimagining education beyond physical borders.
3D Printing in Medical Education
At GUMS, 3D Printing Technology bridges creativity and clinical learning. Students and faculty employ additive manufacturing to produce anatomical models, surgical prototypes, and biomedical teaching aids that simulate real-life conditions.
This innovation enhances spatial understanding, precision practice, and research in Tissue Engineering and Prosthetic Design, reflecting GMUS’s commitment to innovation-oriented pedagogy.
Collaborations with engineering and biomedical laboratories support faculty training and international research networks, positioning GMU as a regional hub for medical simulation and applied health technology.
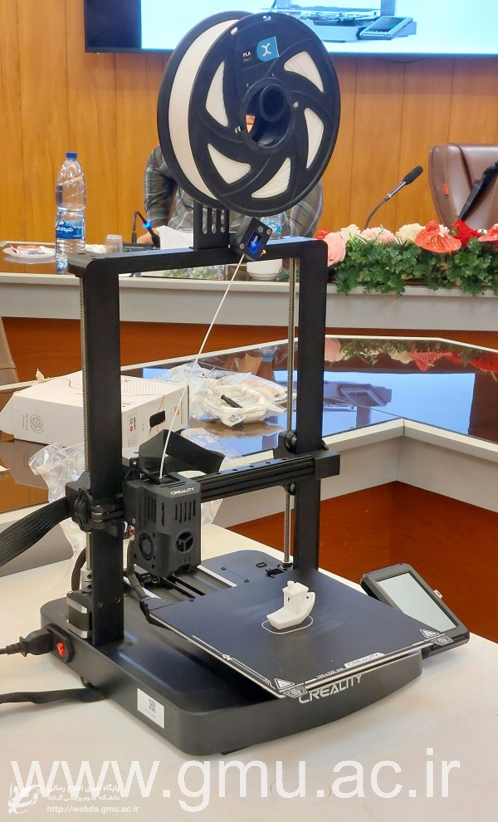


Microlearning: Smart, Focused Education
Microlearning at GUMS delivers concise, high‑impact educational content accessible anytime, anywhere. Through bite-sized instructional videos, infographics, and clinical micro‑cases, learners engage with targeted objectives that strengthen professional competencies in short bursts.
Integrated into both undergraduate and continuing education programs, microlearning supports time‑efficient learning, retention optimization, and AI-assisted assessment — fully consistent with GUMS’s digital transformation agenda and global learning design principles.
Social and Environmental Responsibility in TEL
GMU’s TEL program recognizes that digital evolution must coexist with sustainability.
Thus, the University uses eco‑friendly digital infrastructure, minimizes paper‑based instruction, and designs online learning tools that respect both the learners’ mental health and the planet’s ecological balance.
Looking Ahead — Vision 2030–2040
Under this forward‑looking Vision, GMU aims to expand TEL across all academic programs, develop an AI Health Innovation Hub, and pioneer cross‑national virtual campuses.
The goal is clear: to make GMU a regional leader in intelligent healthcare education, where human values and technology meet to redefine how medicine is taught and practiced.
Empowering learning beyond borders — where technology meets human‑centered education.
In essence, TEL at GMU is not merely a method—it is a movement.
It empowers faculty, transforms learning, strengthens social accountability, and connects medical education to the global digital health revolution—serving the enduring mission of “Health for Humanity and the Planet.”